ENGINES & MACHINERY SPARE PARTS
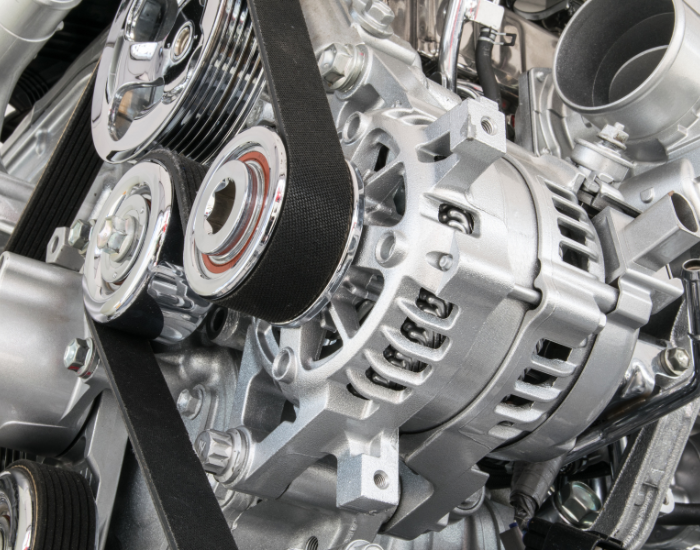

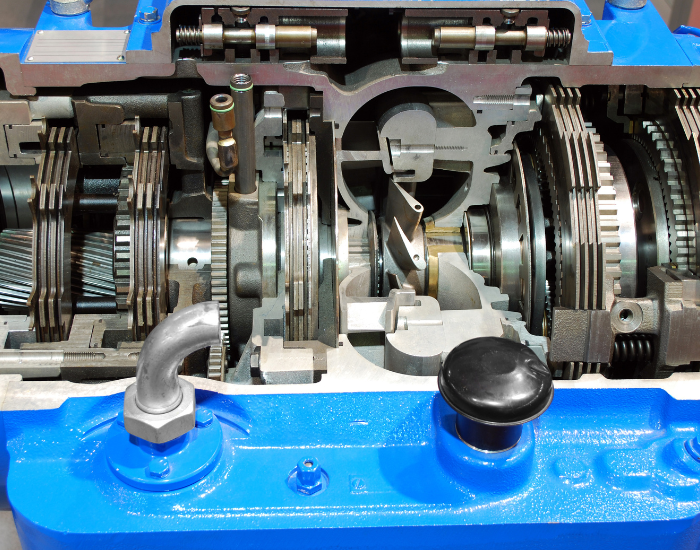
Engines and machinery spare parts are essential components that ensure the proper functioning, maintenance, and repair of mechanical systems used in various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, construction, and agriculture.
These parts can range from simple fasteners to complex assemblies, and their availability and quality are crucial for minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Below is an overview of the types of spare parts, categorization, features, and market considerations.
Categories of Engines & Machinery Spare Parts.
Engine Components
- Pistons: The cylindrical components that move up and down in the engine cylinders.
- Cylinders: The engine’s main component where fuel combustion occurs.
- Crankshafts: Converts linear motion of the pistons into rotational motion.
- Camshafts: Controls the timing of the valve openings and closings.
- Valves: Regulate the flow of air and fuel into the cylinders and exhaust gases out.
- Gaskets and Seals: Prevent leaks by sealing joints between engine components.
Fuel System Parts
- Fuel Pumps: Pumps that supply fuel from the tank to the engine.
- Injectors: Inject fuel into the combustion chamber.
- Carburetors: Mix air and fuel in the correct ratio (for older engines).
- Filters: Clean fuel before it reaches the engine to prevent damage.
Cooling System Parts
- Radiators: Helps dissipate heat from the engine.
- Water Pumps: Circulates coolant through the engine and radiator.
- Thermostats: Regulates the engine’s operating temperature.
- Cooling Hoses: Transfer coolant between components.
Lubrication System Parts
- Oil Pumps: Circulate engine oil to reduce friction and wear.
- Filters: Remove impurities from the engine oil.
- Oil Pans: Collect and store engine oil.
Transmission Parts
- Gears: Facilitate power transmission from the engine to the wheels.
- Clutches: Engage and disengage the power flow.
- Torque Converters: Allows smooth power transfer in automatic transmissions.
Electrical Components
- Batteries: Store electrical energy to start the engine and power electrical systems.
- Alternators: Generate electricity to recharge the battery and power electrical systems.
- Starters: Initiate engine crank and combustion.
- Sensors: Monitor various engine parameters, like temperature and oxygen levels.
Hydraulic Components (for machinery)
- Hydraulic Pumps: Generate pressure to operate hydraulic systems.
- Cylinders: Convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force.
- Hoses and Fittings: Transport hydraulic fluid.
Bearings and Gaskets
- Bearings: Reduce friction between moving parts.
- Gaskets and Seals: Prevent fluid leakage in various components.
Miscellaneous Parts
- Belts and Chains: Transfer power between rotating components.
- Filters (Air and Oil): Clean air and oil for efficient engine operation.
- Fasteners: Bolts, nuts, and screws used to secure components.
Key Features of Spare Parts
- Quality: High-quality materials and manufacturing processes ensure durability and performance.
- Compatibility: Spare parts should be compatible with specific machinery and engine models.
- Availability: Easy access to replacement parts is crucial for minimizing downtime.
- Cost: Availability of a range of parts at different price points, from OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) to aftermarket options.
Conclusion
Engine and machinery spare parts are crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of equipment across various industries. Understanding the types of parts available, their features, and market trends can significantly enhance maintenance practices and operational efficiency. If you have specific needs or questions about certain parts or manufacturers, feel free to ask!
